Wednesday, 14 January, 2026г.
















Где искать: по сайтам Запорожской области, статьи, видео ролики
пример: покупка автомобиля в Запорожье
Wittig reaction mechanism, Ylides, Wittig Salt | Scope & Application | TIFR, CSIR NET, JAM CHEMISTRY
What is Ylides.
Ylides in organic synthesis.
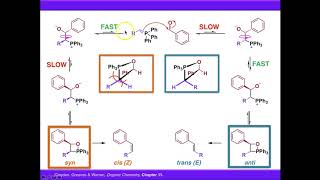
Stability of Ylides.
Wittig reaction mechanism.
Applications.
Problem with solution.
A ylide is a neutraldipolar molecule containing a formally negatively charged atom, usually a carbanion directly attached to a heteroatom with a formal positive charge, usually nitrogen, phosphorus or sulfur, and in which both atoms have full octets of electrons. Ylides are thus 1,2-dipolar compounds, and a subclass of zwitterions. They appear in organic chemistry as reagents or reactive intermediates.
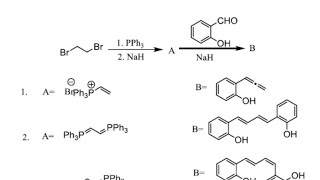
Wittig reaction
The Wittig reaction is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide (often called a Wittig reagent) to give an alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide.
The Wittig reaction was discovered in 1954 by Georg Wittig, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1979.
Baeyer Villiger's oxidation:- https://youtu.be/AZDvB2F-Po0
Wolff Kishner reduction:- https://youtu.be/ceKu3IvZiQg
Stereo chemistry of Diels alder reaction:- https://youtu.be/UZx5X5ZAeE8
Like and comments below
Subscribe now
Share to all
Thanks for watching
Теги:
Wittig reaction for CBSE wittig reaction for NCERT wittig reaction for IIT JEE Main and advanced Wittig reaction for IIT JEE AIPMT AIIMS wittig reaction for IIT Jam CSIR NET GATE Wittig reaction in ENGLISH
Похожие видео
Мой аккаунт


 У вашего броузера проблема в совместимости с HTML5
У вашего броузера проблема в совместимости с HTML5